An Ant’s Path
An ant is positioned at one of the vertices of a cube and wants to get to the opposite vertex. If the edges of the die have length 1, what is the shortest distance the ant needs to travel?
We unfold a cube to get a cross-shaped figure. Then, the problem is to find the shortest path between two points separated by a horizontal distance of 2 units and a vertical distance of 1 unit.
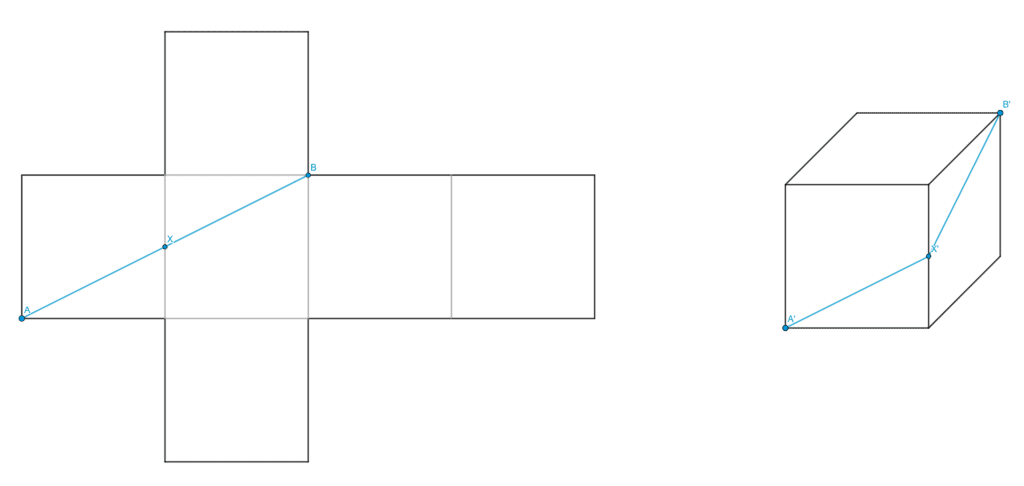
It is easy to see that the path in question is the one passing through the middle of the edge between the start and end points, and which has a distance of √5.